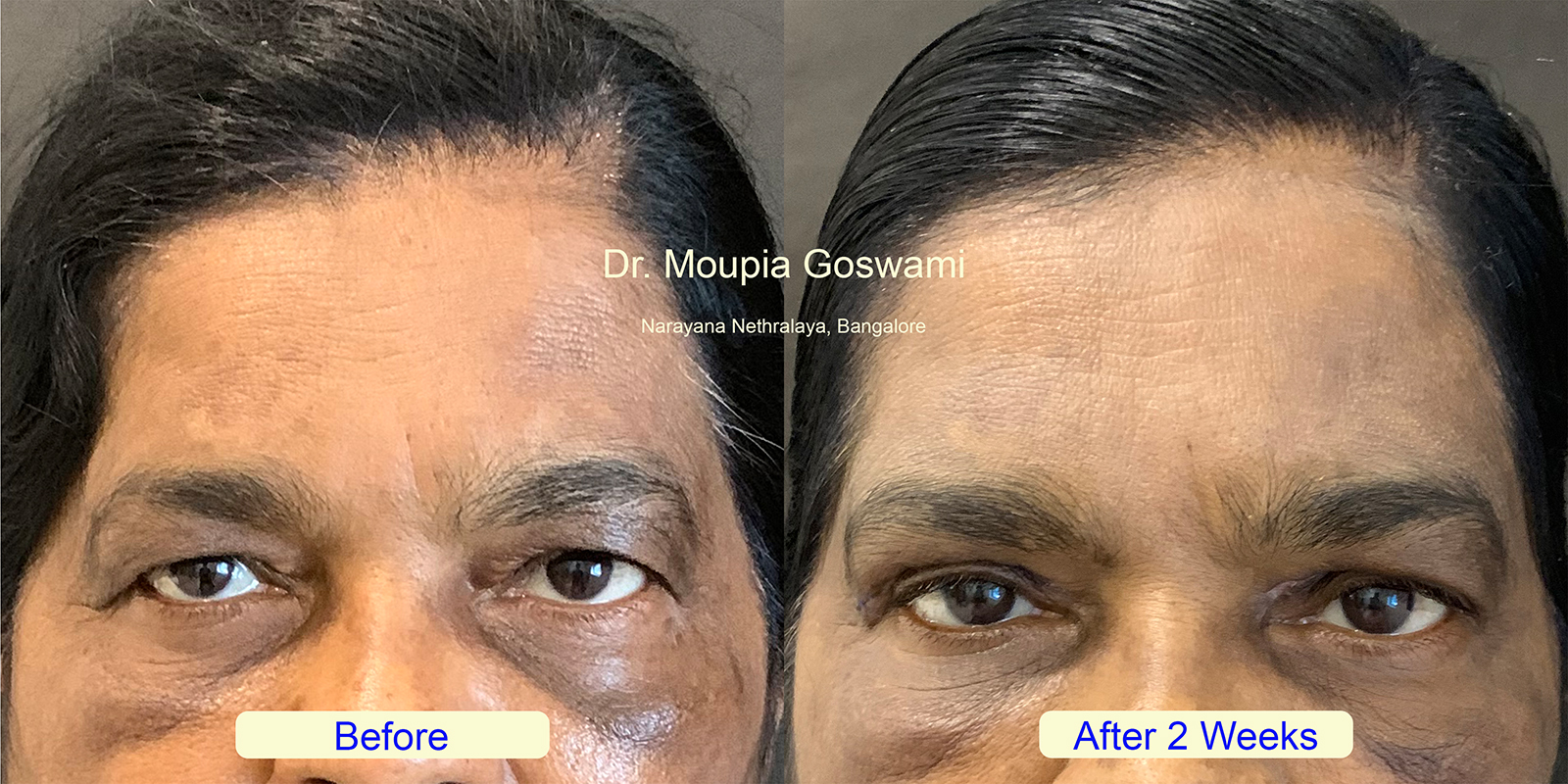
Hooded eyes are a natural eyelid shape where the skin of the upper eyelid folds down over the crease, partially or completely obscuring it. This can give the eyes a heavier or smaller appearance. Hooded eyes can be an inherited trait or develop with age as the skin loses firmness and begins to sag.
While hooded eyes are a normal and common feature, in some cases, they may obstruct vision if the drooping skin becomes more severe. Many individuals with hooded eyes explore options to enhance their appearance or improve functionality. These options range from makeup techniques that accentuate the eyes to surgical procedures like blepharoplasty, which lifts and reshapes the eyelids for a more refreshed and open look.