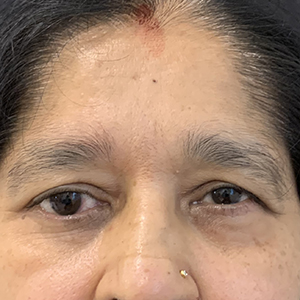
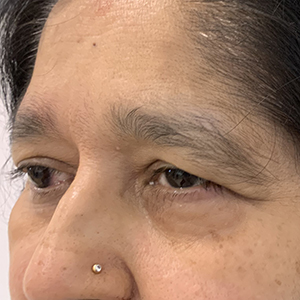
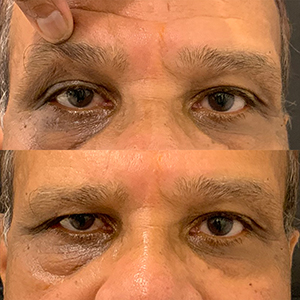
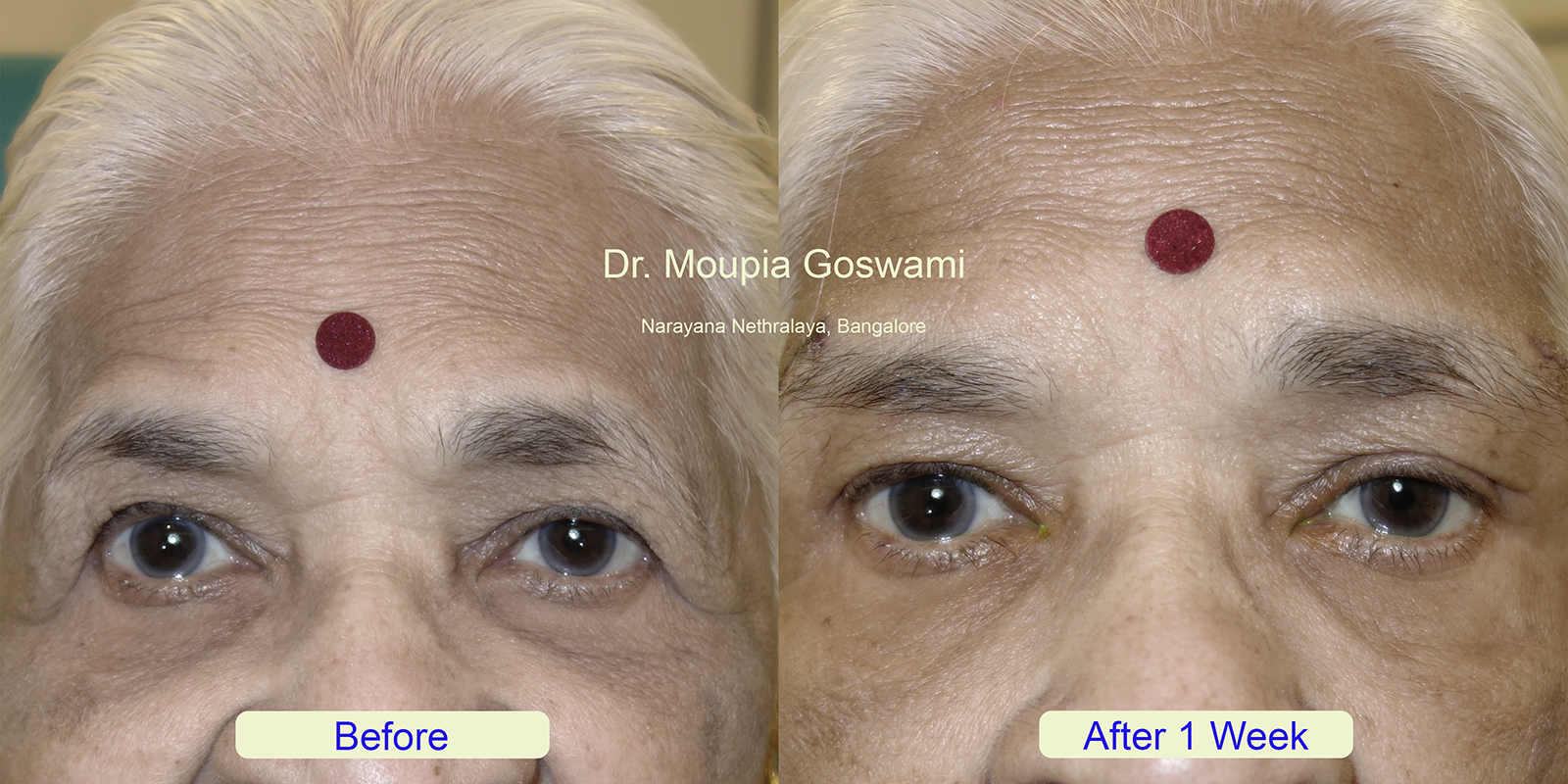
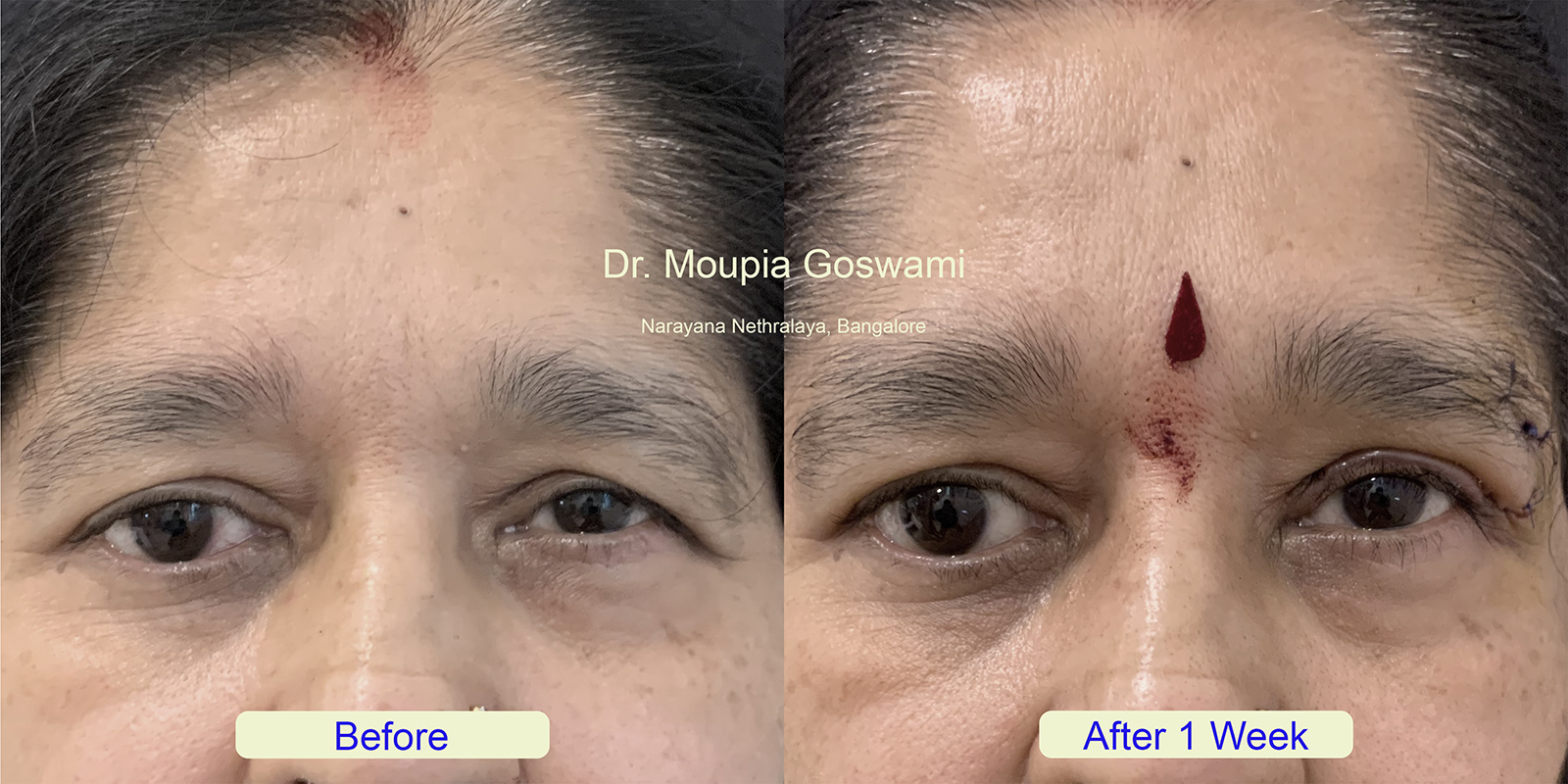
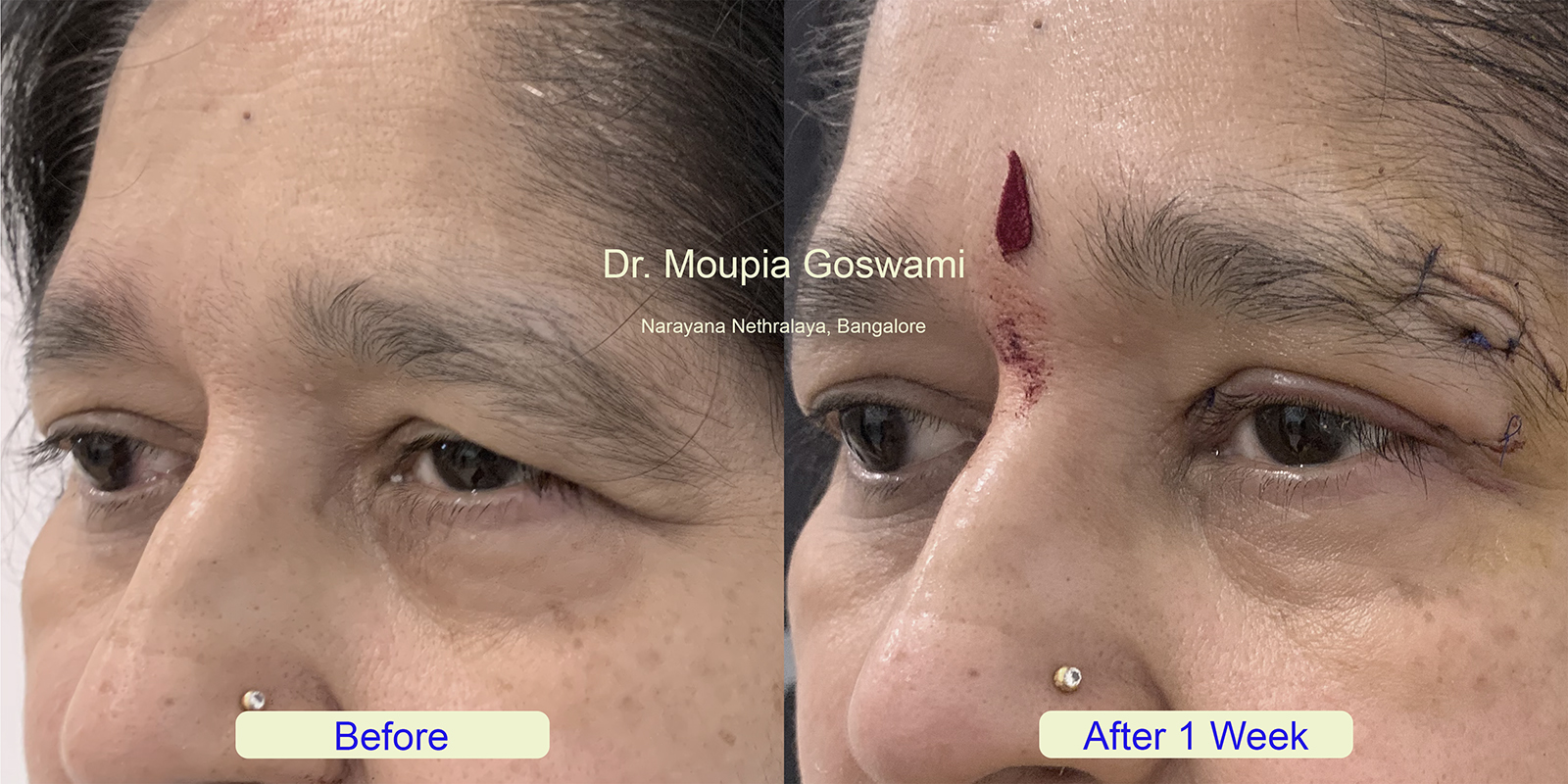
Sagging eyebrows, also known as droopy brows or brow ptosis, occur when the eyebrows descend below their natural position, giving the face a tired, sad, or aged appearance. This condition is often caused by the natural aging process, where the skin and underlying tissues lose elasticity, and the muscles that support the brows weaken. Factors such as genetics, repeated facial expressions, and environmental damage can also contribute to the drooping of the eyebrows.
In more severe cases, sagging eyebrows may partially obstruct vision, making it more than just a cosmetic concern. Treatments for sagging eyebrows range from non-surgical options, such as Botox or dermal fillers, to surgical procedures like a brow lift. These solutions aim to restore the natural arch and position of the brows, rejuvenating the appearance and enhancing facial symmetry.